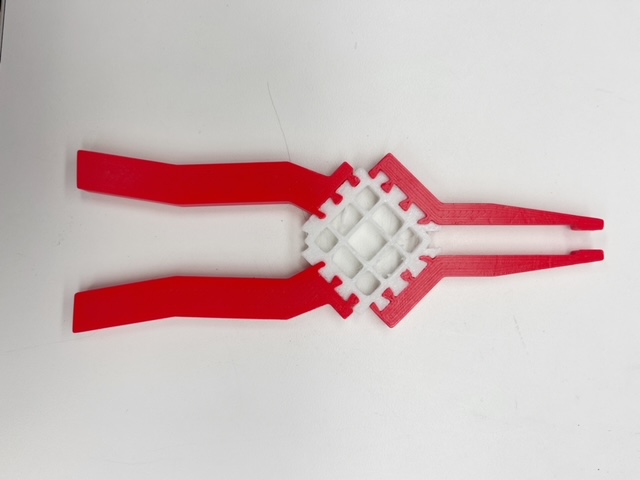
Multimaterial Pliers
Details
-
About This Project
In this project, pliers were designed in Autodesk Fusion 360 with a rigid handle component and a flexible spring component to ensure functionality. These components were then either printed separately on a Voron 3D printer and assembled or printed using a print-in-place technique on a maker space printer with the capability of using different materials in one print. Print-in-place technology is a 3D printing method which creates fully assembled, moving parts in a single print cycle, removing the need to assembling post print.
An important aspect of the project is using different materials for different components in the pliers. These different materials all have different mechanical properties. Using multiple materials in a design such as this one can increase functionality, durability and strength, ergonomics, corrosion resistance, and weight reduction. When using multiple materials in 3D printing, print-in-place technology further allows one to print multiple parts with different compositions in a single manufacturing process without the need for assembly. This is a great solution for interlocking or jointed components, such as gears or chains.
Another beneficial aspect of print-in-place technology is the ability for parts to be fully functional straight off the print bed. Materials play a crucial role in the success of print-in-place 3D printing. The combination of materials must be carefully selected to ensure that the parts can withstand the stresses of printing and subsequent use. Flexible materials such as TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) are often used for joints or hinges due to their elasticity and durability. For rigid parts, materials like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) are preferred for their strength and ease of printing. In order to further determine material compatibility, it is important to look at factors such as chemical and mechanical compatibility, shrinkage and cooling rates, and surface energies of materials. If two materials have similar said factors, then they will print and adhere to each other better.
Print-in-place applications extend across various industries, from consumer products to aerospace. A particularly exciting application of print-in-place and multilateral technology is for creating complex medical prosthetics. Multi-material printing allows prosthetics to be custom fitted to the user’s specific anatomical measurements, ensuring a comfortable fit. By using print-in-place techniques, prosthetics are designed with integrated joints that adapt to the user’s movements. Additionally, this method optimizes lightweight designs by utilizing the best material for lattice structures, and other geometries creating an ideal set-up for prosthetic manufacturing.
Overall, this project is a microscopic view of the many applications and the huge potential for multimaterial and print-in-place technology. This project reveals how these technologies can be harnessed to create useful tools.
-
Design & Print Process
The multi-material pliers were designed using PLA for the rigid parts, comprising the handles and jaws, and TPU for the flexible component. This flexible spring component features a diamond-shaped center with a cross pattern, optimized for shear resistance, ensuring that when manipulated in a specific way, the jaws securely clamp down around a resistor, which typically has a diameter of 0.5 mm. The jaw width of 6.5 mm is particularly suited for gripping resistors because it allows for precise manipulation without causing damage to these small components.
The overall length of the pliers was designed to be 170 mm, with a handle length of 70 mm, ensuring they comfortably fit in an average person’s hand. This ergonomic design facilitates ease of use and reduces hand fatigue during prolonged working. The jaw length of 50 mm and an inner flexible spring side length of 30 mm in the TPU material are calculated to provide optimal performance and durability. The flexible and rigid parts are integrated using dovetail joints with a minimal offset, ensuring a strong and reliable connection that enhances the tool’s functionality.
While print-in-place technology could have been used for this design, the design process allowed for simple post-print assembly. Therefore, this device was printed on a Voron printer and assembled after the print was complete. The flexible spring component was printed using TPU 95A with an infill of 20% and a .6 mm diameter nozzle. The settings were adjusted to the right bed and melting temperature for TPU 95A. The rigid handle and jaw components were printed using PLA with an infill of 20% and a .6 mm diameter nozzle. The settings were adjusted to the right bed and melting temperature for PLA.
-
Device Specifications
| Measurement Type | Value (mm) |
|---|---|
| Full Length | 170 |
| Handle Length | 70 |
| Jaw Length | 50 |
| Spring Component Side Length | 30 |
| Jaw Capacity | 6.5 |
| Maximum Handle Width | 65 |
CAD Model
Pictures of Product
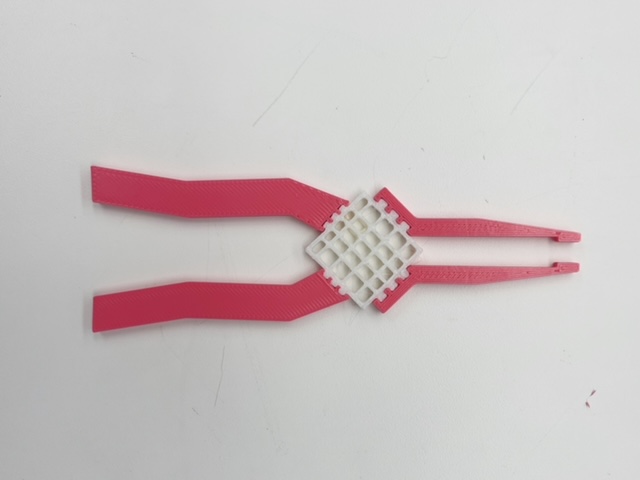
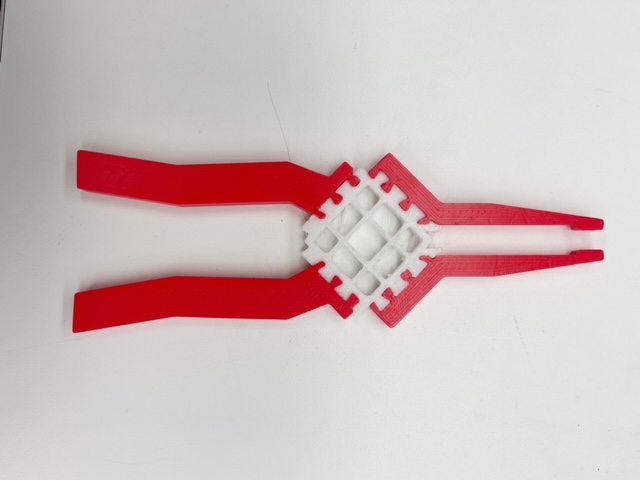

Functionality of Multimaterial Plier Product